TCFD
Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures
Established by the Financial Stability Board (FSB) in 2015 to develop recommendations that enable companies to disclose climate-related financial risks and opportunities in a clear, consistent, and comparable way, TCFD aims to improve the transparency of climate-related financial information across markets, supporting better-informed investment, credit, and insurance underwriting decisions.

Understanding TCFD
Climate change presents physical and transition risks that can have significant financial implications for organisations. The TCFD framework provides a structured approach to help companies identify, assess, and disclose these climate-related risks and opportunities in their mainstream financial filings.
The framework is principles-based, built around four core pillars:
- Governance
How the organisation’s governance structure oversees climate-related risks and opportunities.
- Strategy
The actual and potential impacts of climate-related issues on business, strategy, and financial planning.
- Risk management
How climate-related risks are identified, assessed, and managed.
- Metrics and targets
The metrics and targets used to assess and manage climate-related risks and performance.
Who can apply this Framework?
TCFD is designed for all sectors and company sizes:
Publicly listed companies
Financial institutions (e.g., asset managers, banks, insurers)
Private companies with climate exposure
Public sector bodies and large non-profit organisations
TCFD is particularly relevant to businesses operating in high-impact sectors such as energy, transport, agriculture, real estate, and finance.
Universal or local?
TCFD is a globally recognised framework and has been adopted in over 95 jurisdictions. Its recommendations are voluntary but have been incorporated into regulation or stock exchange requirements in countries such as the United Kingdom, Japan, New Zealand, Singapore, Switzerland, and the European Union.
Read more

Praise and recognition for TCFD
Endorsed by public and private entities
TCFD is widely endorsed by governments, financial regulators, central banks, stock exchanges, and standard-setting bodies. More than 4,000 organisations worldwide support TCFD, including major institutional investors and global corporates.
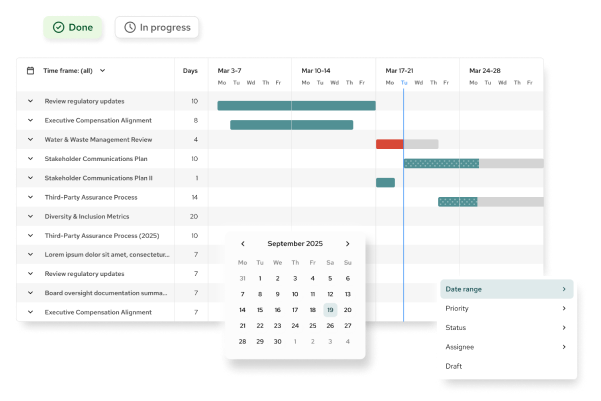
1. How to use?
Organisations typically follow these steps to align with TCFD:
Conduct a climate risk assessment
Identify physical and transition risks relevant to your business.
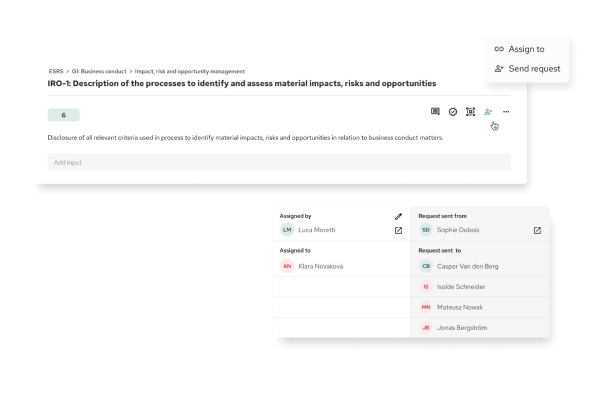
Develop Climate Governance Structures
Assign oversight and establish responsibility at board and management levels.
Analyse Scenarios
Use climate scenarios (e.g., 1.5°C, 2°C pathways) to explore potential business impacts.
Integrate into Strategy and Risk Management
Embed climate risks into strategic planning and enterprise risk management.
Measure and Monitor
Establish metrics and targets to track exposure and progress.
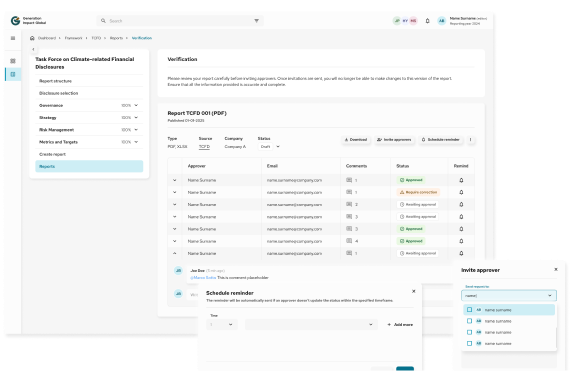
Report Publicly
Disclose climate-related information through annual reports or sustainability disclosures, aligned with the four TCFD pillars.
Learn more2. Benefits
TCFD reflects the following perks on any company or industry that follows its methodology:
Investor Confidence
Strengthens transparency and trust by addressing investor demand for climate-related financial disclosure.
Risk Awareness
Helps organisations understand how climate risks may impact operations, supply chains, and long-term resilience.
Strategic Planning
Encourages long-term thinking through scenario analysis and integration with risk management.
Regulatory Readiness
Positions organisations to comply with emerging reporting requirements, including ISSB, EU CSRD, and national regulations.
Market Recognition
Improves access to capital by demonstrating robust climate governance and preparedness.
Key features
Frequently Asked Questions
General Questions
1. Is TCFD mandatory?
While TCFD is voluntary at its core, many countries and regulators have integrated it into mandatory disclosure rules for listed and large entities.
2. Can SMEs use TCFD?
Yes, although the framework is more commonly applied by large and listed companies, SMEs can adapt TCFD principles to their scale and resources.
3. How is TCFD different from other frameworks?
TCFD focuses specifically on climate-related financial disclosures, with a clear structure around governance, strategy, risk, and metrics. It complements broader frameworks like GRI or SASB.
4. What is scenario analysis in TCFD?
Scenario analysis explores the resilience of a company’s strategy under different climate outcomes (e.g. 1.5°C, 2°C, or 4°C warming), helping to anticipate long-term financial impacts.
5. Where should we publish TCFD disclosures?
Ideally, in annual financial filings or integrated sustainability reports. Some jurisdictions mandate disclosure within specific regulatory documents.
6. Is TCFD only relevant to carbon-intensive industries?
No. Climate risks can affect all sectors—via supply chain disruption, resource availability, changing regulations, and reputational pressure.
7. How does TCFD align with ISSB Standards?
IFRS S2 Climate-related Disclosures, developed by the ISSB, is based on TCFD recommendations and expands on them to form a new global baseline.
8. What support is available to implement TCFD?
Guidance documents, capacity-building programmes, and tools are available via the TCFD Knowledge Hub and various regional regulatory bodies.
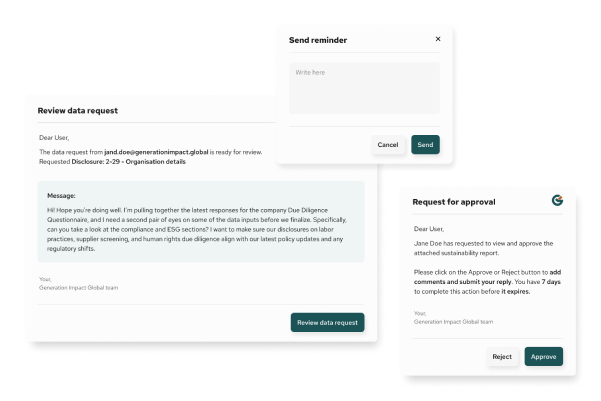
9. Can TCFD disclosures improve investor engagement?
Yes. TCFD-aligned reporting provides investors with the forward-looking, financially relevant information they need to assess climate-related risk exposure.
10. What if my company is just starting with climate reporting?
Begin by assessing climate governance and identifying priority risks. TCFD allows for a gradual, scalable approach based on your maturity and capacity.
Interoperability
What other Frameworks are compatible with TCFD?