Build KPI calculation logic
Define KPI calculation logic before reporting begins
What is the KPI logic builder
The KPI logic builder in QB-EDGE™ allows users to configure how key performance indicators are derived directly from questionnaire data within the system.
Instead of calculating KPIs later in spreadsheets or BI tools, calculation logic is defined upstream using structured inputs and controlled rules. This supports consistency, traceability, and audit-ready results.
KPI logic is commonly used for ESG, sustainability, regulatory, and operational reporting where calculation consistency and auditability are required.

How KPI calculation logic works
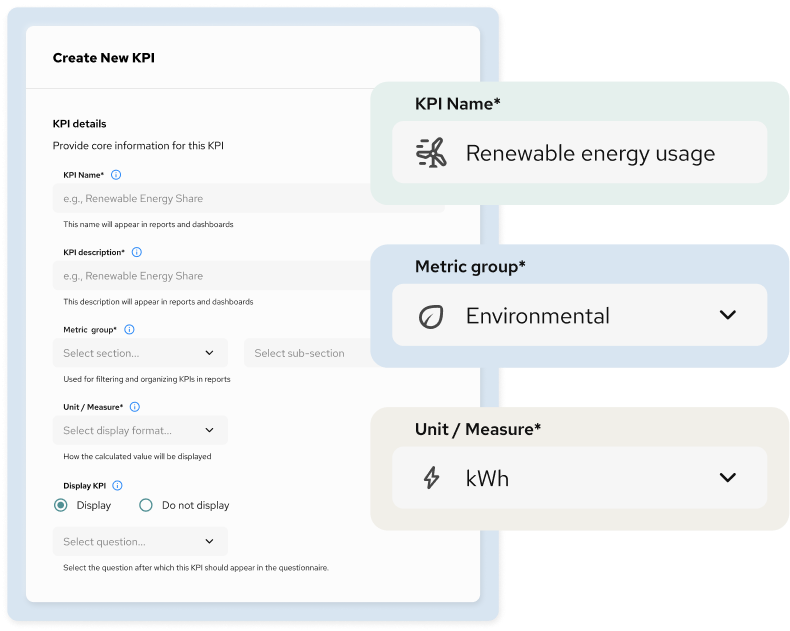
Create the KPI
Clarify what the KPI measures and how it is interpreted
KPIs are defined using clear business logic that specifies what each indicator measures and why it matters. Names and descriptions are structured to remain consistent and understandable across reports, dashboards, and management discussions.
Each KPI is then assigned to a metric group (section and subsection) and configured with the appropriate unit or display format.
Select source data
Reference structured inputs with clear data lineage
Each KPI is linked to one or more source fields from structured questionnaires or templates. Source fields are referenced using unique identifiers, so KPI calculations are based on defined and traceable inputs.
KPI inputs can be configured to:
- use a single source field directly
- combine multiple source fields in one calculation
- reference values from different reporting periods, where applicable
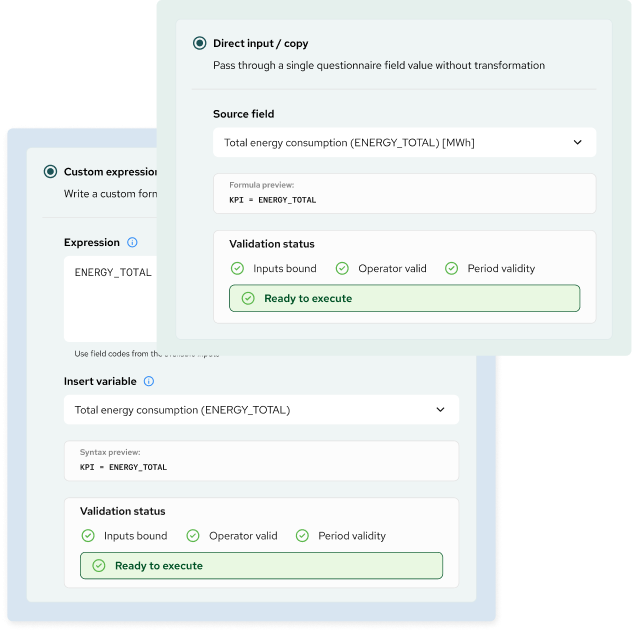
Define calculation logic
Specify how KPI values are derived from source fields
KPI values can be defined using one of two calculation methods:
- Direct pass-through, where the KPI mirrors the value of a single source field without transformation
- Custom calculation logic, where users define expressions using predefined field codes and standard operators
The expression builder supports arithmetic operations and controlled syntax, allowing calculations to be defined in a structured and repeatable way.
Only valid operators and compatible field types can be used, preventing invalid or inconsistent logic.
Validate inputs and
calculation logic
Confirm data availability, syntax integrity, and period alignment
Before a KPI can be executed, the system runs a set of validation checks, including:
- verification that all referenced source fields are available
- validation of calculation syntax and operators
- confirmation that referenced values align with the selected reporting periods
Each KPI displays a validation status that highlights configuration issues before execution. This pre-execution validation reduces errors and limits the need for downstream corrections.
Apply logic across periods and reporting scope
Reuse consistent KPI definitions across time and organisational structures
Once defined, KPI logic can be applied consistently:
- across multiple reporting periods
- across entities, branches, or organisational units
- across recurring data-collection and reporting cycles
KPI definitions are reusable and do not require reconfiguration for each new cycle, supporting consistent application over time and across organisational structures.
Why teams use the KPI logic builder:
Move calculations out of spreadsheets
KPI logic is defined centrally and reused, rather than recreated in Excel for each reporting cycle.

Improve transparency and auditability
Calculation rules are explicit, visible, and reviewable. There are no hidden formulas or undocumented adjustments.

Reduce rework and inconsistencies
By validating inputs and logic before execution, teams avoid reconciliation issues and late-stage corrections.

Support consistent performance measurement
The same KPI definition is applied across teams, entities, and periods, enabling comparability and reliable analysis.
Typical use cases
- Financial and operational KPIs
- Efficiency and productivity metrics
- Cost and resource indicators
- Ratios derived from multiple data inputs
- Recurring internal or external reporting
- ESG and sustainability KPIs (e.g. emissions, energy, water, waste)
- Regulatory and compliance reporting metrics (GRI, ESRS, SFDR, ISSB)
- Portfolio-level and entity-level performance tracking
- Year-over-year and period-over-period comparisons
- KPIs reused across funds, business units, or subsidiaries
- KPIs requiring audit-ready calculation logic and traceability
What this feature is and is not
The KPI logic builder is used to define and validate KPI calculation rules
It standardises how KPI values are derived so they can be reused consistently across reports, dashboards, and exports.
It is not:
- a dashboard or visualisation tool
- a BI or analytics platform
- a manual calculation or modelling workspace
How it works with templates
KPI logic is defined on top of controlled data structures, including:
Questionnaire templates,
which provide consistent source data
Predefined field types,
which standardise inputs across entities
Reporting scope,
which control how values are aligned over time
KPI calculations are therefore based on structured and validated data with defined metadata, rather than free-form inputs or unmanaged spreadsheet logic.
Once defined, the same KPI logic can be reused across templates, entities, and reporting periods without reconfiguration.
The better way to handle KPIs
Define KPI calculation logic.
Use it every reporting cycle.
Request Demo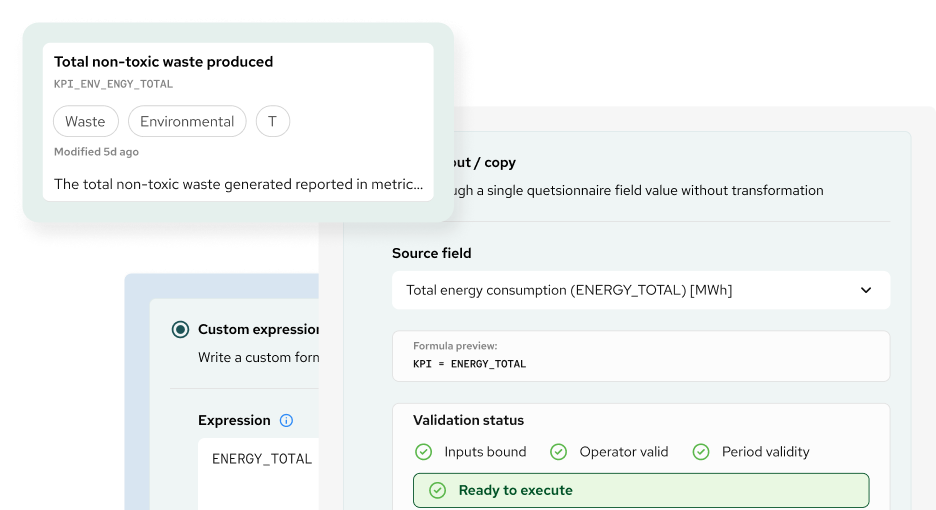
Questions related to KPI Logic Builder
What is the KPI logic builder?
The KPI Logic Builder is a structured configuration tool used to define, calculate, and validate KPI formulas based on governed input data. It ensures that KPIs are calculated consistently and can be reused across reports, periods, and entities.
How is KPI logic different from KPI tracking or dashboards?
KPI logic defines how a KPI is calculated. Tracking tools and dashboards focus on displaying results. The KPI Logic Builder sits upstream, ensuring that KPI values are derived from validated, structured data before they are visualised or reported.
What data can be used as input for KPI calculations?
KPI calculations use data collected through structured questionnaire templates, predefined field types, controlled reporting periods, and defined organisational scopes. Free-text or unvalidated spreadsheet inputs are intentionally excluded.
What types of calculations are supported?
The tool supports common KPI calculation logic, including sums, averages, ratios, percentages, weighted values, thresholds, and conditional logic based on defined rules and metadata.
Are KPI calculations validated before use?
Yes. KPI logic is validated against field definitions, data types, reporting scope, and period rules to ensure calculation consistency and prevent structural errors before results are used in reports or exports.
Can KPI logic be reused across reporting cycles?
Yes. Once defined, KPI logic can be reused across reporting years and cycles, ensuring methodological consistency and reducing manual rework over time.
Can the same KPI logic be applied across multiple entities or units?
Yes. KPI logic can be applied across multiple companies, funds, business units, or organisational levels, provided the underlying data structure and scope definitions are aligned.
Who typically defines KPI logic?
KPI logic is usually defined by sustainability, ESG, impact, finance, or reporting teams, often in collaboration with compliance or data governance stakeholders.
Does using the KPI logic builder replace Excel?
No. The KPI Logic Builder does not aim to replace Excel as a general analysis tool. It replaces ad-hoc and uncontrolled KPI calculations by providing a governed, auditable, and reusable calculation layer within the reporting system.
Is technical or coding knowledge required?
No. The tool is designed for business and reporting users. KPI logic is configured through structured options and rules, without requiring coding or scripting.
How does KPI logic work with templates?
KPI logic is built on top of questionnaire templates and predefined fields. This ensures that KPI calculations are always linked to validated data inputs with clear metadata, scope, and reporting periods.
What are typical use cases for the KPI logic builder?
Typical use cases include ESG and sustainability reporting, regulatory disclosures, internal performance measurement, portfolio-level aggregation, and ensuring consistent KPI definitions across frameworks and reporting cycles.


